
Pakistan is currently experiencing one of the fastest solar adoption rates in the world. By March 2025, the country’s net-metered rooftop solar capacity alone reached an astonishing 4.9 Gigawatts (GW) — nearly doubling the previous year’s total.
Analysts predict that solar will become Pakistan’s largest electricity source in 2025, contributing over 25% of total national production. Faced with rising electricity costs and frequent power outages, individuals, businesses, and farmers are fueling a massive solar “boom” that’s reshaping the entire national grid.
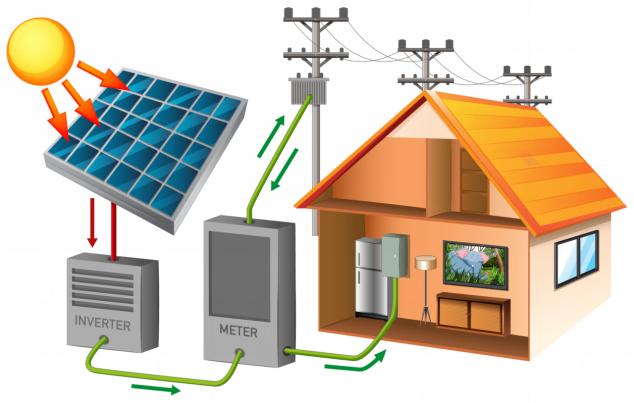
The On-Grid System is the most common and cost-effective choice for properties connected to the national grid — perfect for reducing monthly electricity bills.
It uses a Grid-Tied Inverter that synchronizes with the utility waveform, converting solar energy into AC power. The electricity is first consumed locally, and any surplus is exported back to the grid through Net Metering — earning credits and cutting costs dramatically.
💰 Pros: Lowest upfront cost, fastest ROI (Return on Investment), and no battery maintenance required.
⚠️ Limitation: Automatically shuts down during grid outages (anti-islanding), so no backup power.
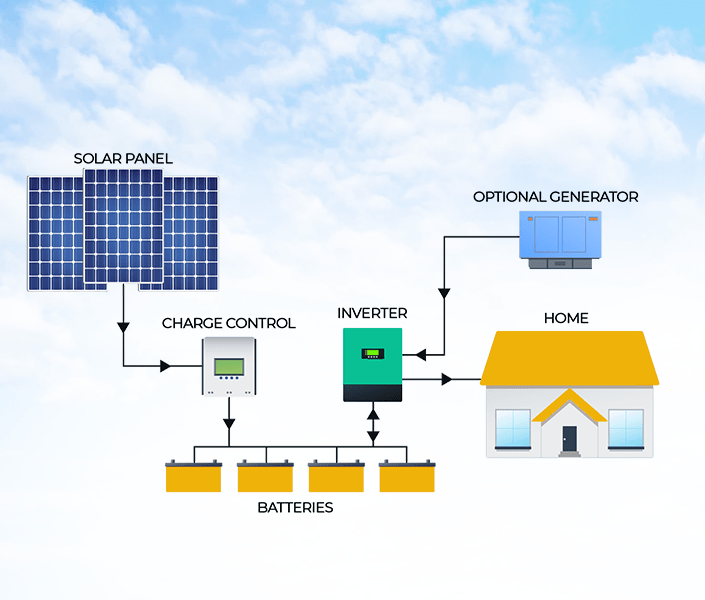
The Off-Grid System provides complete energy independence — ideal for areas with no grid access or highly unreliable connectivity.
It uses a Charge Controller to regulate the current from solar panels to a Battery Bank, storing energy for use at night or on cloudy days. Since it’s disconnected from the utility grid, it offers freedom from electricity tariffs and regulations.
🌾 Best for: Remote farmhouses, isolated commercial sites, and solar-powered irrigation systems.
⚠️ Trade-off: Higher upfront cost (battery bank + inverter), regular maintenance, and battery replacement.
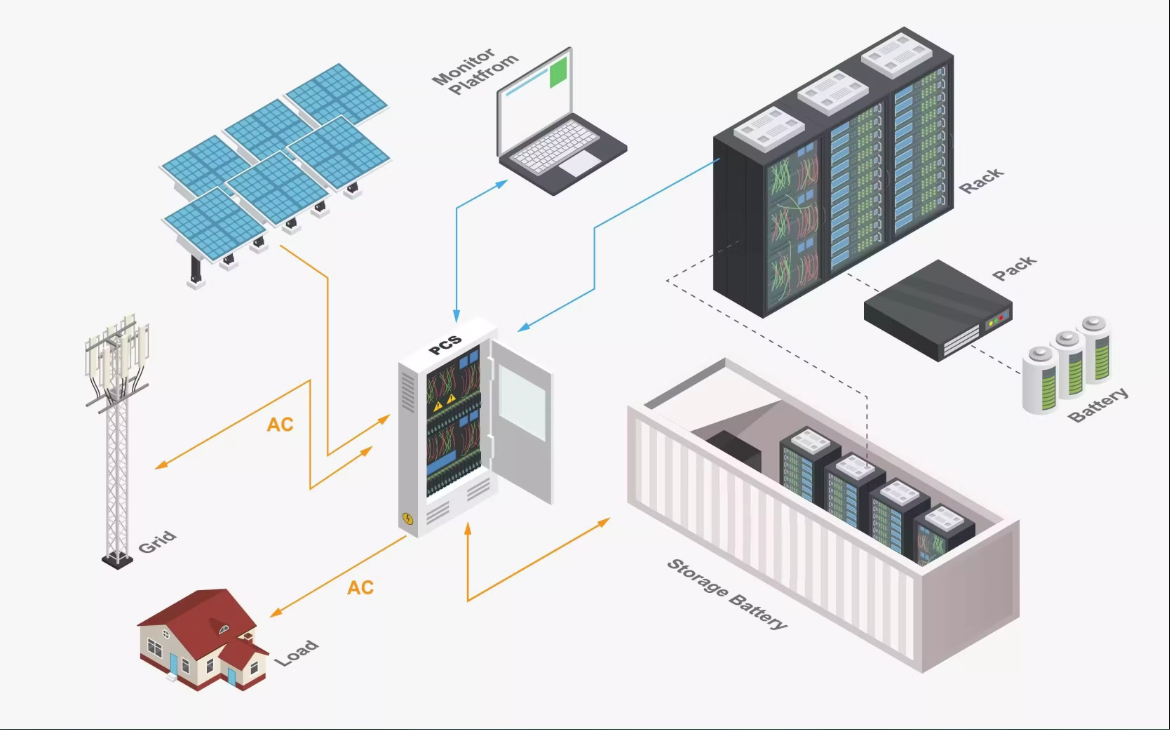
The Hybrid System is becoming Pakistan’s most popular option — combining the savings of an On-Grid system with the reliability of backup power.
Using a Hybrid Inverter and Battery Energy Storage System (BESS), it manages three power sources: solar, battery, and grid. It prioritizes solar usage, charges batteries, and exports extra energy when available.
During outages, it automatically creates a local “micro-grid” to keep essential loads powered.
💡 Advantages: Supports Net Metering + provides backup during load-shedding.
💸 Investment: Slightly higher cost, but justified by continuous power and long-term value.
As Pakistan’s energy landscape evolves, going solar isn’t just a smart investment — it’s a move toward true energy independence.
To make the most of this transformation, you need a trusted partner experienced in both Solar PV and Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS).
NRTC Energies specializes in custom-designed, reliable, and efficient solar solutions that empower homes, businesses, and farms across Pakistan.
📞 Ready to harness the power of the sun?
Contact NRTC Energies today to find the perfect solar system for your needs.

Backed by NRTC’s decades of leadership in security and telecom, we stepped into the solar industry with a mission: to help solve Pakistan’s energy crisis with smart, sustainable power. Today, we make solar energy accessible, affordable, and reliable for homes, businesses, industries, and farms across the country.

Call us for support

UAN Number

Email Us Here

Haripur, Islamabad, Rawalpindi, Lahore, Peshawar, Quetta, Karachi, Multan, Turbat